Food Production & Processing
Food Production & Processing
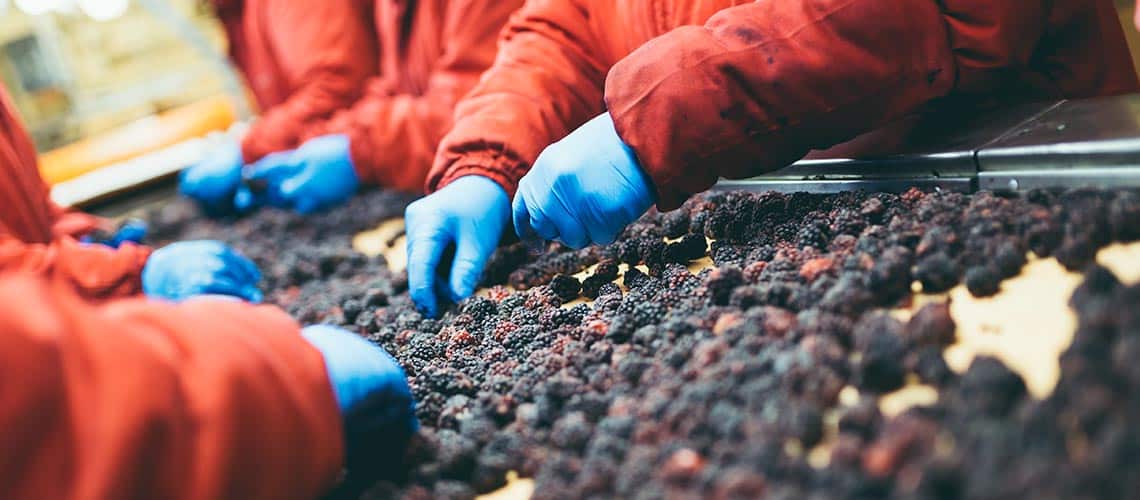
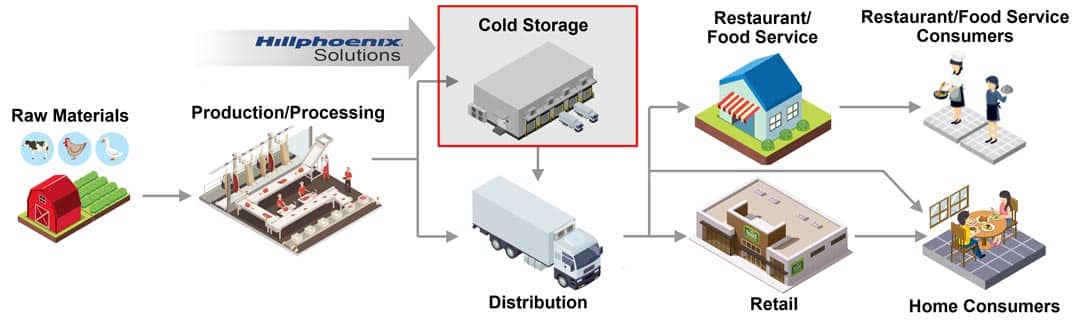
The Food & Beverage industry consists of those companies that transform raw agricultural commodities or semi-processed food products into a broad range of consumer-ready food and beverage products. Food and beverage production and processing is a part of the overall food and beverage supply chain (see image below) where finished products are ultimately distributed to the population of consumers worldwide.
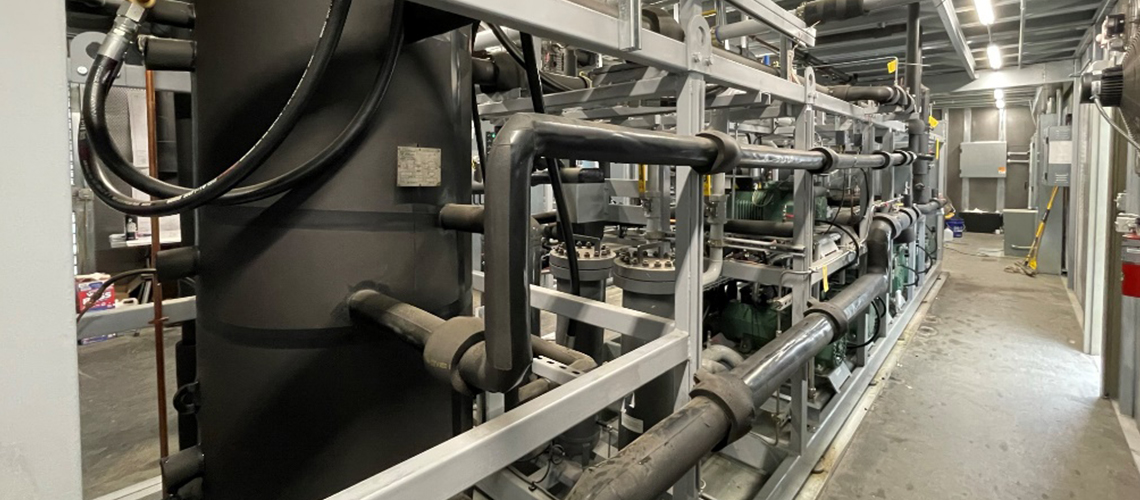
Hillphoenix food and beverage processing solutions are designed to provide safe, cost-effective, efficient systems that provide temp and humidity control in a processing room environment and promote sustainable management of food through reducing food waste. Whether it’s a cold storage need in the process, or blast freezing to freeze the food so quickly that the water molecules inside don’t have a chance to damage the food itself, Hillphoenix has the solution. Choose between a Hillphoenix industrial parallel rack design utilizing either HFC or HFO refrigerants or go “all-natural” with a Hillphoenix CO2 transcritical booster system solution to meet your specific needs.
The Food & Beverage production and processing segment serves a wide gamut of retail and commercial outlets ranging from food sold at the grocery stores to food services (e.g., cooked meals served at restaurants, institutions, and events) to the fast-growing direct-to-consumer (DTC) approach, ultimately feeding a global population approaching eight billion people worldwide.
What Role Does Hillphoenix Refrigeration Play in Food and Beverage Production and Processing?
The fundamental purpose of refrigeration in industrial food and beverage production and processing is to keep food cold. Cold temperatures help food stay fresh longer by slowing down the activity of bacteria, thus making it less susceptible to spoilage and waste, reducing the incidence of foodborne disease, and improving the taste of the food.
The “cold chain”, with regards to food and beverage, refers to the process of managing the temperature of perishable products in order to maintain quality and safety from the point of origin through the distribution chain to the final consumer. Hillphoenix industrial refrigeration equipment plays a vital role in maintaining food and beverage optimal temperatures in refrigerated warehouse applications. Having a set of strict standards in cooling is key to reducing spoilage and food waste and reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses caused by bacteria.
Hillphoenix helps companies ensure the integrity of the cold supply chain with innovative, traditional and sustainable Cold Storage refrigeration solutions. Whether it be parallel rack systems employing synthetic refrigerants (HFC/HFO) or the all-natural refrigerant Hillphoenix CO2 booster system, Hillphoenix has designed and installed custom, centralized industrial refrigeration equipment cooling millions of cubic feet of warehouse and distribution space throughout North America.
Proper cooling practices throughout the cold chain are not just about food safety. They also ensure that food quality isn’t degraded by any environmental factors (e.g., humidity) resulting in spoilage or contamination and subsequent food waste. Maintaining temperature control of the “cold chain” on the production floor is critical and extends to the post-manufacturing transportation and storage of the produced products.
There are a variety of refrigeration processes employed in the production and processing of food. Among some of the most common are:
- Pre-cooling
- Chilling
- Freezing
- Supercooling and Superchilling
- Other food processes
Which Refrigerants Are Typically Used in a Food and Beverage Production and Processing Industrial Refrigeration System?
Small Facilities
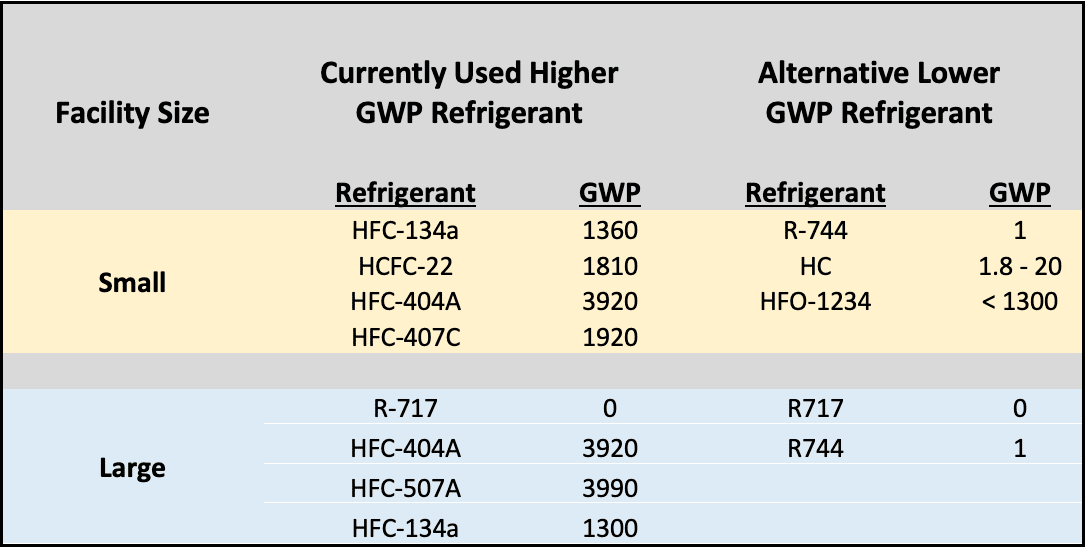
Non-flammable refrigerants with low toxicity are widely used currently, such as those belonging to the family of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). However, due to their high Global Warming Potential (GWP), regulatory mandates are requiring countries to progressively reduce or phase out their use.
Alternatives to HFCs would include the use of low-GWP and natural refrigerants:
- Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) is a family of refrigerants with a very low GWP, however, their availability, current cost, and mild flammability behavior limit their widespread use. In addition, the long-term accumulation of their decomposition residuals in the environment has not been studied and evaluated.
- Hydrocarbons (e.g. Isobutane, Propane) are used in some applications, but only for very low refrigerant charges due to their high flammability.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) is rapidly coming on strong. The low environmental impact and cost-effective operation as well as the progress made in the designing of CO2 loops makes this a realistic and promising sustainable alternative.
Hillphoenix offers parallel rack refrigeration systems utilizing a choice between HFC, HFO, or CO2 refrigerants that offer cost-effective, efficient solutions for the needs of smaller facilities.
Larger Facilities
Ammonia has traditionally been used in large cooling production loops. The downside to using ammonia though has always been its toxicity. When it comes to reducing the hazards and regulatory burdens associated with this refrigerant, some approaches have been used for a long time, while others have been advancing recently:
- For chilling, the use of a cooling distribution loop based on a secondary refrigerant (such as propylene glycol) is a technology that has existed for a long time. It significantly reduces the quantity of ammonia present in the system, and therefore dramatically improves the overall safety of the facility.
- For freezing, the use of two-stage, cascade systems with, for instance, HFC-R134a or ammonia in the high-temperature stage and CO2 in the low-temperature stage, also reduces the ammonia charge and its inherent risk.
- The progress made in designing CO2 loops has increased the use of full CO2 refrigeration systems, especially for freezing and low-temperature warehouses. Hillphoenix manufactures an all-natural refrigerant CO2 booster system that can be found serving the needs of many such applications in the industrial world today.
What Is the Outlook for the Food and Beverage Production and Processing Market?
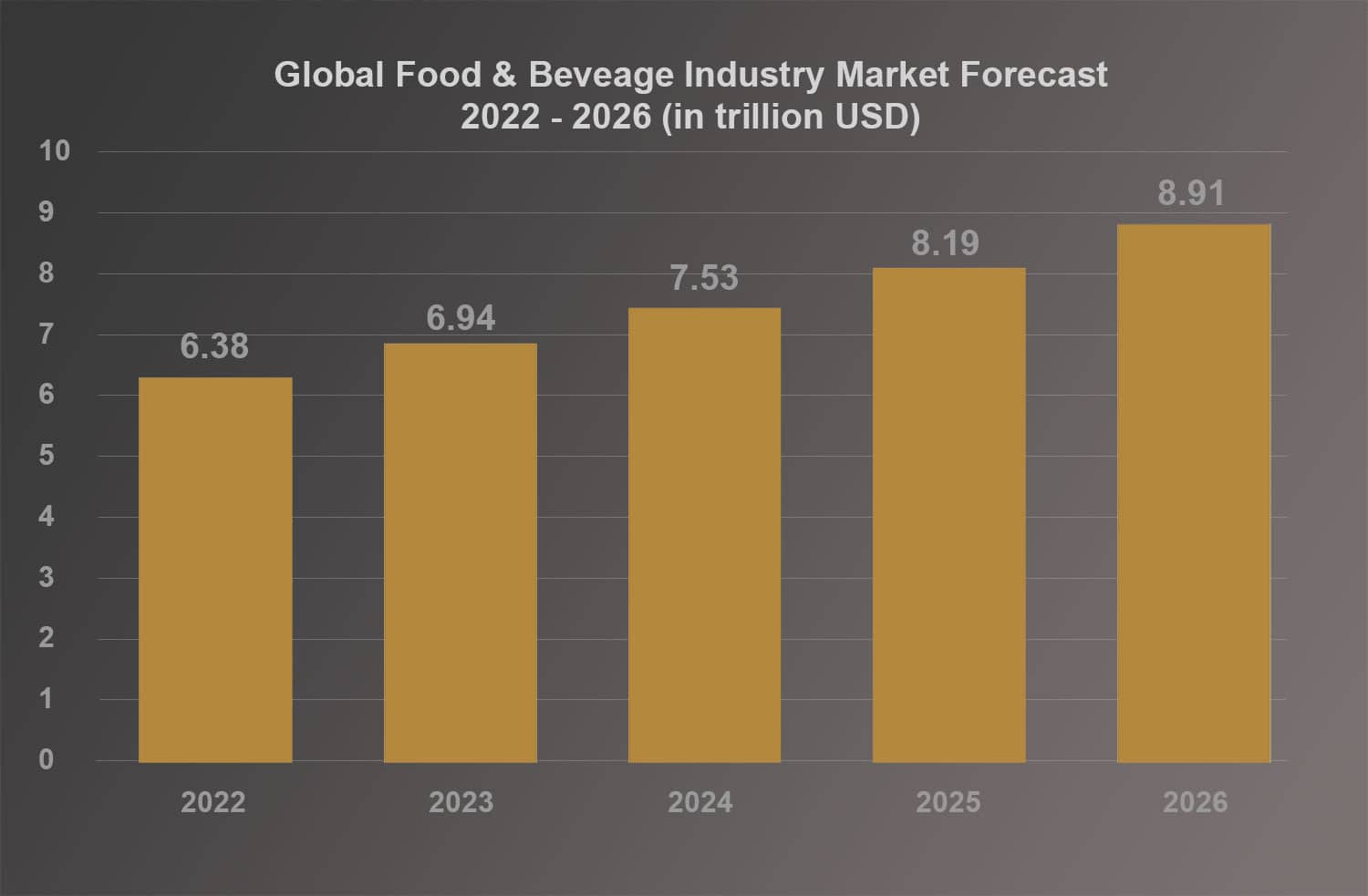
The global food and beverages market size is expected to grow from $5,817.4 billion in 2021 to $6,383.49 billion in 2022. The market size is expected to continue to grow to $8,905.5 billion in 2026 at a CAGR of 8.7% (see graph below). The largest regional contributor to the market’s total revenue in 2021 was Asia Pacific while Western Europe followed in second place.
What Role Does Hillphoenix Refrigeration Play in Food and Beverage Production and Processing?

The fundamental purpose of refrigeration in industrial food and beverage production and processing is to keep food cold. Cold temperatures help food stay fresh longer by slowing down the activity of bacteria, thus making it less susceptible to spoilage and waste, reducing the incidence of foodborne disease, and improving the taste of the food.
The “cold chain”, with regards to food and beverage, refers to the process of managing the temperature of perishable products in order to maintain quality and safety from the point of origin through the distribution chain to the final consumer. Hillphoenix industrial refrigeration equipment plays a vital role in maintaining food and beverage optimal temperatures in refrigerated warehouse applications. Having a set of strict standards in cooling is key to reducing spoilage and food waste and reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses caused by bacteria.
Hillphoenix helps companies ensure the integrity of the cold supply chain with innovative, traditional and sustainable Cold Storage refrigeration solutions. Whether it be parallel rack systems employing synthetic refrigerants (HFC/HFO) or the all-natural refrigerant Hillphoenix CO2 booster system, Hillphoenix has designed and installed custom, centralized industrial refrigeration equipment cooling millions of cubic feet of warehouse and distribution space throughout North America.
Proper cooling practices throughout the cold chain are not just about food safety. They also ensure that food quality isn’t degraded by any environmental factors (e.g., humidity) resulting in spoilage or contamination and subsequent food waste. Maintaining temperature control of the “cold chain” on the production floor is critical and extends to the post-manufacturing transportation and storage of the produced products.
There are a variety of refrigeration processes employed in the production and processing of food. Among some of the most common are:
- Pre-cooling
- Chilling
- Freezing
- Supercooling and Superchilling
- Other food processes
Which Refrigerants Are Typically Used in a Food and Beverage Production and Processing Industrial Refrigeration System?
Small Facilities
Non-flammable refrigerants with low toxicity are widely used currently, such as those belonging to the family of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). However, due to their high Global Warming Potential (GWP), regulatory mandates are requiring countries to progressively reduce or phase out their use.
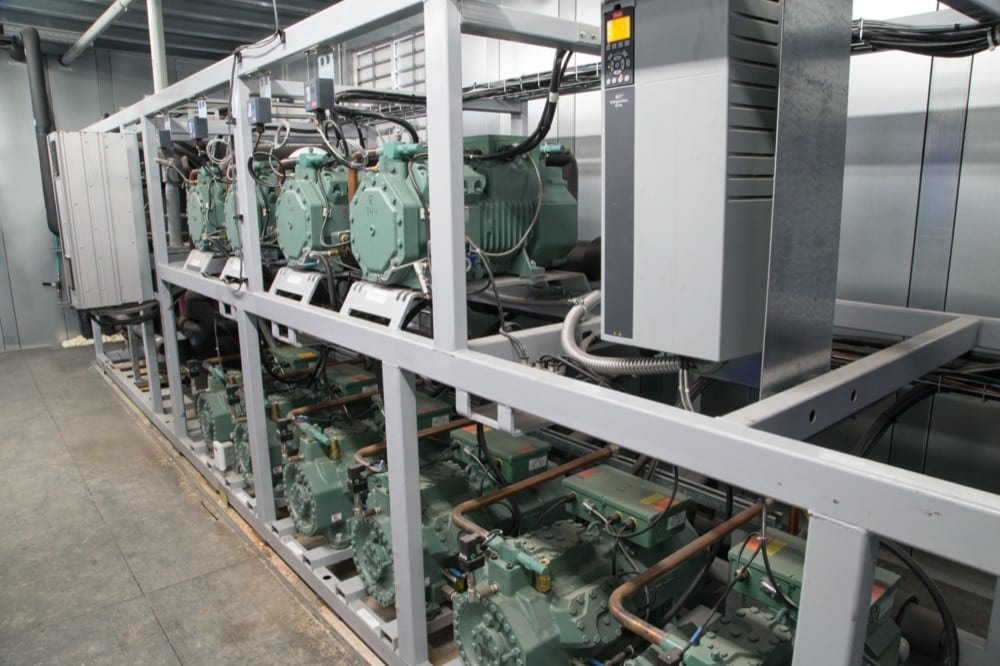

Alternatives to HFCs would include the use of low-GWP and natural refrigerants:
- Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) is a family of refrigerants with a very low GWP, however, their availability, current cost, and mild flammability behavior limit their widespread use. In addition, the long-term accumulation of their decomposition residuals in the environment has not been studied and evaluated.
- Hydrocarbons (e.g. Isobutane, Propane) are used in some applications, but only for very low refrigerant charges due to their high flammability.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) is rapidly coming on strong. The low environmental impact and cost-effective operation as well as the progress made in the designing of CO2 loops makes this a realistic and promising sustainable alternative.
Hillphoenix offers parallel rack refrigeration systems utilizing a choice between HFC, HFO, or CO2 refrigerants that offer cost-effective, efficient solutions for the needs of smaller facilities.
Larger Facilities
Ammonia has traditionally been used in large cooling production loops. The downside to using ammonia though has always been its toxicity. When it comes to reducing the hazards and regulatory burdens associated with this refrigerant, some approaches have been used for a long time, while others have been advancing recently:
- For chilling, the use of a cooling distribution loop based on a secondary refrigerant (such as propylene glycol) is a technology that has existed for a long time. It significantly reduces the quantity of ammonia present in the system, and therefore dramatically improves the overall safety of the facility.
- For freezing, the use of two-stage, cascade systems with, for instance, HFC-R134a or ammonia in the high-temperature stage and CO2 in the low-temperature stage, also reduces the ammonia charge and its inherent risk.
- The progress made in designing CO2 loops has increased the use of full CO2 refrigeration systems, especially for freezing and low-temperature warehouses. Hillphoenix manufactures an all-natural refrigerant CO2 booster system that can be found serving the needs of many such applications in the industrial world today.
What Is the Outlook for the Food and Beverage Production and Processing Market?

The global food and beverages market size is expected to grow from $5,817.4 billion in 2021 to $6,383.49 billion in 2022. The market size is expected to continue to grow to $8,905.5 billion in 2026 at a CAGR of 8.7% (see graph below). The largest regional contributor to the market’s total revenue in 2021 was Asia Pacific while Western Europe followed in second place.
Food Production & Processing Insights
Meat Processing Plant Expansion Made Simple With CO2 Expertise from Hillphoenix Industrial
When a boutique meat processor needed to double capacity, they [...]
What Role Does Refrigeration Play in Food and Beverage Production and Processing?
The fundamental purpose of refrigeration in industrial food and beverage [...]
What Is the Outlook for the Food and Beverage Production and Processing Market?
Expectations for growth in this market are high over the [...]
Which Refrigerants Are Typically Used in a Food Process & Production Refrigeration System?
Small Facilities Non-flammable refrigerants with low toxicity are widely used [...]
Refrigeration Solutions for the Food Production & Processing Industries

CO2 Booster Systems
The Hillphoenix transcritical booster system, employing parallel rack architecture, utilizes only one refrigerant—the abundantly available, completely sustainable and economical CO2. CO2 is neither flammable nor toxic, making it ideal in terms of installation and system operation. Advansor is the most reliable and energy-efficient CO2 refrigeration system on the market.

Parallel Racks
Parallel Racks by Hillphoenix® are custom-designed platforms that offer the ultimate in flexibility, performance, and efficiency to the industrial refrigeration market. They are built around multiple compressors — however many the installation requires — linked in parallel to provide a host of benefits that are unique to this very robust architecture.

Synthetic HFC/HFO Systems
Until the recent emergence of CO2 as a viable industrial refrigerant alternative, industrial refrigeration systems have traditionally relied upon two refrigeration coolant technologies for decades: Ammonia for very large systems while synthetic halocarbon refrigerants account for the rest.

PowerCenter
PowerCenters are a completely modularized electrical distribution system in a custom enclosure. Multiple designs allow indoor and outdoor installation. Integrated electrical enclosures replace a conventionally built room while reducing footprint and clearance restrictions.

PowerWall
PowerWall is a cost-effective, flexible power distribution and control system for a wide variety of industrial applications. Totally integrated units arrive at the job site completely wired and pre-tested, reducing a significant part of the field contractor’s time.

Mechanical Centers
Mechanical Centers, designed for either indoor or outdoor placement, give you immediate flexibility as to where you wish to locate your refrigeration system equipment – on a slab behind your facility, a mezzanine inside, or on the roof.